Ligaments play a vital role in stabilizing joints and supporting the musculoskeletal system. Among these crucial structures is the
Understanding Ligaments
Before we dive into the specifics of the LCL, let’s take a moment to understand the general role of ligaments in our bodies. Ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of connective tissue that connect bones to other bones, providing stability and limiting excessive movements in joints. They act as natural stabilizers, preventing dislocations and maintaining the proper alignment of bones during movement.
What is the Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)?
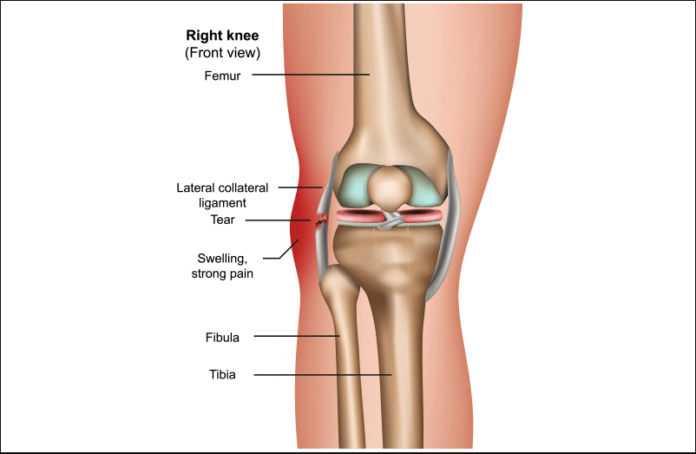
The Lateral Collateral Ligament, commonly referred to as the LCL, is one of the major ligaments in the human knee joint. It is located on the outer side of the knee and connects the femur (thighbone) to the fibula (a bone in the lower leg). The primary function of the LCL is to stabilize the knee joint and prevent excessive sideways movement.
Anatomy of the Lateral Collateral Ligament
The Lateral Ligament is a robust and resilient structure composed of collagen fibers. It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the femur and extends downwards to attach to the head of the fibula. This unique placement allows the LCL to provide lateral stability to the knee joint.
Functions of the Collateral Ligament
The main function of the LCL is to resist varus forces, which are forces that push the knee joint inward. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the knee’s stability during activities involving lateral movements, such as pivoting, cutting, and side-stepping. Additionally, it works in conjunction with other ligaments to support the overall integrity of the knee joint.
Common Injuries to the Lateral Ligament
LCL injuries often occur due to sudden, traumatic events that place excessive stress on the ligament. These injuries are common in athletes, especially those who participate in sports with frequent changes in direction or contact. The severity of LCL injuries can range from mild sprains to complete tears.
Diagnosing LCL Injuries
To accurately diagnose an LCL injury, a medical professional will conduct a thorough physical examination and may order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. This process helps determine the extent of the injury and guides the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Lateral Ligament Injuries
The treatment for LCL injuries depends on the severity of the damage. Mild to moderate sprains can often be managed with conservative treatments such as rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), and supportive braces. However, severe tears may require surgical intervention to repair the ligament and restore knee stability.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Following an LCL injury, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery. Physical therapy exercises are essential to regain the knee joint’s strength, flexibility, and stability. Adherence to the rehabilitation plan is vital for a successful return to regular activities.
Preventing LCL Injuries
While some LCL injuries are unavoidable, there are measures that individuals can take to reduce the risk of such injuries. These include regular conditioning exercises, proper warm-up routines, using appropriate protective gear, and maintaining good form during physical activities.
Differences between LCL and MCL Injuries
It’s essential to distinguish between LCL and Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) injuries, as the treatment approaches may vary. This section will highlight the key differences between these two types of injuries and their respective management.
LCL Injuries in Sports
Sports enthusiasts are particularly susceptible to LCL injuries due to many athletic activities’ dynamic and high-impact nature. We will explore some common sports that put individuals at risk of LCL injuries and how athletes can protect themselves.
LCL Injury in Non-Athletic Populations
LCL injuries are not exclusive to athletes; they can also occur in everyday situations. This section will discuss how non-athletic individuals may sustain LCL injuries and how they can seek appropriate treatment.
Surgical Intervention for Severe LCL Injuries
In cases of severe LCL tears where conservative treatments are insufficient, surgical intervention may be the best course of action. This section will delve into the surgical options available and what patients can expect from the procedure and recovery process. Read more…
Conclusion
The Lateral Collateral Ligament is a crucial component of the knee joint, playing a vital role in providing stability during various movements. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common injuries can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent damage and seek appropriate treatment when needed. Whether you’re an athlete or someone seeking to understand human anatomy better, the LCL is undoubtedly an essential aspect to explore.