In the world of human anatomy, ligaments play a crucial role in connecting bones and stabilizing joints. One such vital ligament is the (UCL). Ulnar collateral ligament, exploring its anatomy, common injuries, treatment options, and rehabilitation. Whether you’re an athlete, a medical enthusiast, or someone dealing with UCL issues, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights.
The collateral ligament (UCL) is a critical structure found in the elbow joint. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining stability and preventing excessive side-to-side movement of the joint. Understanding the UCL is essential, especially for athletes involved in sports that require repetitive arm motions, such as baseball pitchers.
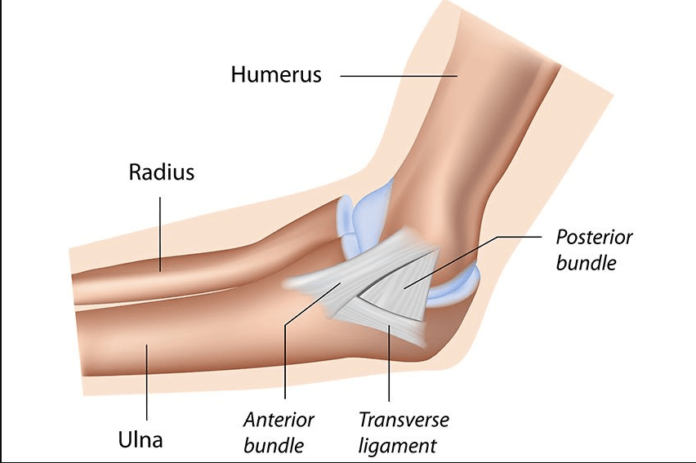
Anatomy of the Ulnar Collateral Ligament
The UCL is a complex ligament consisting of three primary components: the anterior bundle, posterior bundle, and transverse ligament. These structures work together to connect the humerus to the ulna, forming a stable hinge joint at the elbow.
Functions of the Ulnar Collateral Ligament
The primary function of the UCL is to resist valgus stress, which occurs when the elbow is forced outward. This ligament is essential for activities that involve throwing, swinging, and any motion that places stress on the inner side of the elbow.
Common Injuries to the UCL
UCL injuries are prevalent among athletes, especially baseball players. The most common UCL injury is a partial or complete tear, often Overuse and repetitive stress can lead to UCL injuries.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of a UCL injury is crucial for timely intervention. Symptoms may include pain and a feeling of instability. Sometimes, an MRI to assess the severity of the injury.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Approaches
- Rest and Rehabilitation: Mild UCL injuries can often be managed with rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Bracing: The use of a brace or splint can provide support to the injured UCL during the healing process.
Surgical Interventions
- Tommy John Surgery: This surgical procedure involves replacing the damaged UCL with a graft from another part of the body, such as the forearm or hamstring tendon.
- Internal Brace: A newer technique involves augmenting the UCL repair with an internal brace to enhance stability and reduce the risk of re-injury.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation is a critical phase in the recovery process. It focuses on strengthening the elbow, improving range of motion, and gradually returning to sports-specific activities. A tailored rehabilitation program is essential for a successful recovery.
Prevention and Maintenance
To reduce the risk of UCL injuries, athletes should incorporate proper warm-up routines, maintain overall fitness, and practice good throwing mechanics. Additionally, regular check-ups with a sports medicine specialist severe. Read more…
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can UCL injuries occur in non-athletes?
- Yes, while common among athletes, UCL injuries can also affect individuals in occupations or activities that involve repetitive elbow stress.
- How long does it take to recover from Tommy John surgery?
- Recovery times vary, but it can take up to 12-18 months to fully return to competitive play.
- Are there any non-surgical alternatives for UCL injuries?
- Yes, mild UCL injuries can often be managed with conservative treatments, but the approach depends on the severity of the injury.
- Can UCL injuries be prevented entirely?
- While they cannot be entirely prevented, the risk can be significantly reduced with proper conditioning, technique, and regular monitoring.
- Are there any long-term consequences of UCL injuries?
- Without appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, UCL injuries.
Conclusion
The ulnar collateral ligament is a critical component of the elbow joint, and understanding its anatomy, function, and potential injuries is essential. Whether you’re an athlete aiming to protect your UCL or someone seeking information on treatment options, this article provides valuable insights. Remember, early diagnosis and appropriate intervention can lead to successful recoveries from UCL injuries.